
Moran Towing Corporation acquired Bisso Towboat Co, as it aims to accommodate growing needs of New Orleans and the Lower Mississippi River communities.Moran was founded in 1860 and is privately owned and operated. It offers ship assist services in 17 ports along the U.S. East and Gulf Coasts and has operated in New Orleans since 2006.

In the early hours of Friday, June 20, Great Lakes Towing tugs conducted an efficient refloating operation of the foreign-flagged freighter SUNNANVIK, which had become lodged in the narrow mouth of the Cuyahoga River near the East Bank of the Flats.At approximately 12:43 a.m., the 9,000-ton SUNNANVIK became wedged in the canal, temporarily disrupting traffic.

Van Oord's new offshore wind installation vessel Boreas was officially christened on June 18 in Rotterdam. The event marked a milestone in Van Oord’s commitment to enhancing the energy transition. In addition, Van Oord announced that it had become the first marine contractor to receive approval on science-based targets for its decarbonization approach. The Boreas was christened by Ms.

How can the global energy grid keep pace with fast-growing demand from new data centers supporting artificial intelligence (AI) and cloud computing? Nuclear energy and coastal waters offer a potential answer.The potential for floating nuclear-powered data centers is explored in depth in the latest research from ABS and Herbert Engineering.

The Mexican ship which crashed into New York's Brooklyn Bridge over the weekend did not make distress calls before ramming into the bridge, the head of Mexico's navy said on Tuesday, but rather called for support.Navy chief Raymundo Morales, speaking at Mexican President Claudia Sheinbaum's morning press conference

A Mexican Navy sailing ship festooned with lights and a giant flag crashed into the landmark Brooklyn Bridge on Saturday night, shearing the top of its masts, killing two people and injuring several others, New York City Mayor Eric Adams said.Videos online showed the training vessel Cuauhtémoc as it approached the bridge over the East River, close to the Brooklyn side of the span
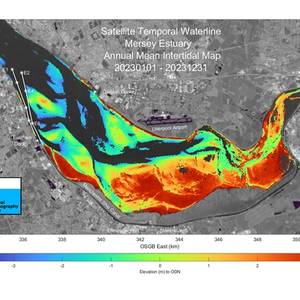
Scientists at the UK’s National Oceanography Centre (NOC) in Liverpool have used satellite data to create insight into the Mersey River that will help port operators be smarter about managing complex navigation channels. Through a project focused on Liverpool’s famous river and funded by the UK Space Agency

Incat Hull 096 – the world’s largest battery-electric ship – has been officially launched in Tasmania, Australia.Built for South American ferry operator Buquebus, the 130-meter ferry will enter enters service between Buenos Aires and Uruguay, operating entirely on battery-electric power, carrying up to 2,100 passengers and 225 vehicles across the River Plate.

On April 30, Senator Mark Kelly (D-AZ), together with several original co-sponsors, reintroduced the SHIPS for America Act in the U.S. Senate, first introduced in December 2024, divided into two bills. Companion legislation was also introduced in the U.S. House of Representatives by Rep. Trent Kelly (R-MS) and Rep. John Garamendi (D-CA). This is a major, historic effort to revitalize the U.S.

Benny Cenac Jr.’s Houma based Main Iron Works Company has completed the 10th boat newbuild for Ingram Marine Group. This partnership with Main Iron Works and Ingram began in 2021 and included the construction of 10 new towboats to be completed by the end of 2024. The first towboat, the Adrienne M.

The US Coast Guard is coordinating with local, state and federal agencies in response to the helicopter crash in the Hudson River that occurred Thursday afternoon in New York City near the Holland Tunnel.The tourist helicopter crashed into New York City's Hudson River, killing all six aboard, including three children, Mayor Eric Adams said.

[The following are exerpts and paraphrasing from testimony given by Matthew O. Paxton, President of the Shipbuilders Council of America (SCA), to Congress on the morning of February 26, 2025.]While maritime strength and shipbuilding historically have been a cornerstone of global power, shifting times and geopolitical pressures impact readiness and output.